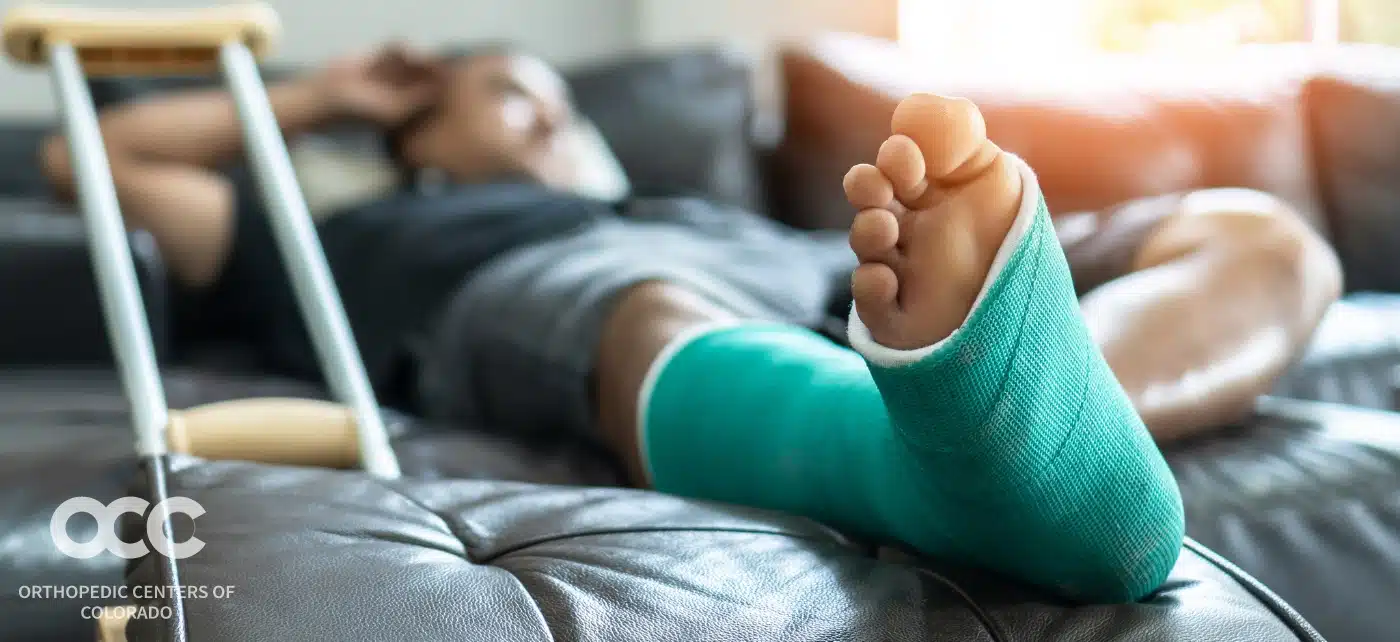
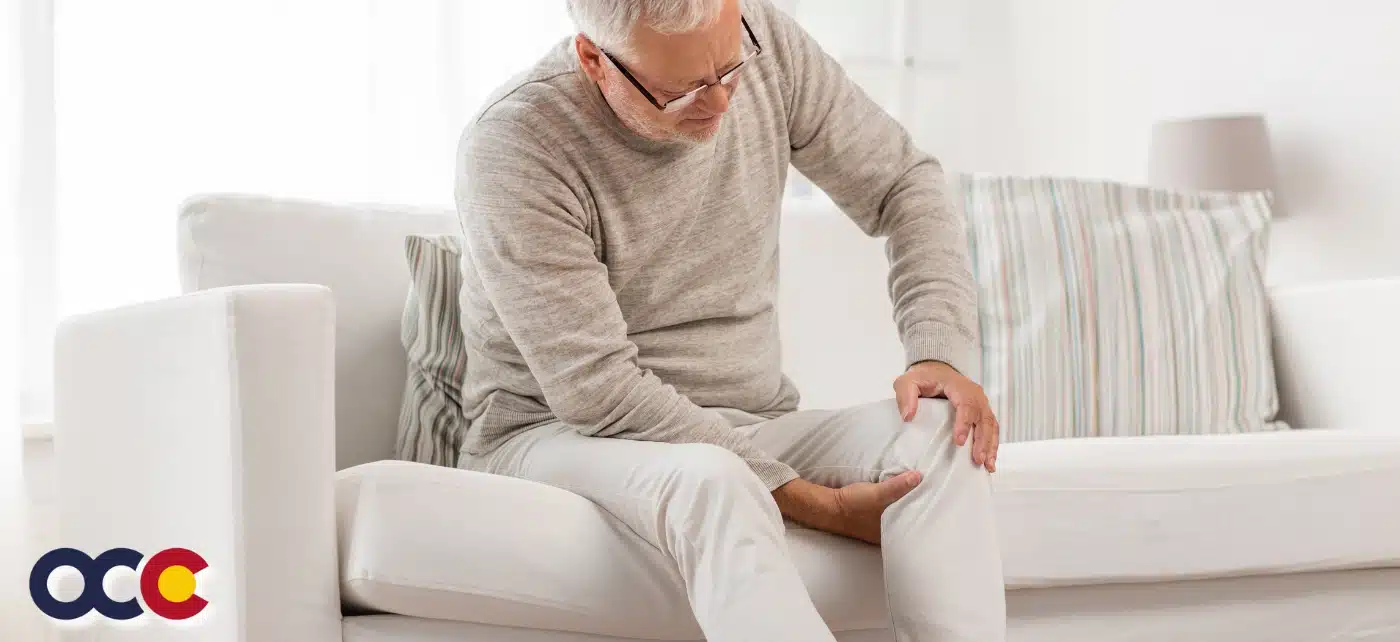
A fracture of the calcaneus, or heel bone, is a serious and disabling injury that can lead to longstanding problems in the foot and ankle. Calcaneus fractures can cause intense pain and make walking more difficult. Without treatment, calcaneus fractures may worsen and further damage the broken bone. Because calcaneus fractures can be hard to treat, it’s imperative getting the best help from the most experienced orthopedic specialists, like those you’ll find at Advanced Orthopedic & Sports Medicine Specialists in Denver, Parker, and Aurora, Colorado. No one needs to suffer from the pain or possible complications of a calcaneus fracture.
OVERVIEW
A calcaneus fracture is one or more small breaks in the heel bone (calcaneus). Calcaneus fractures are relatively uncommon, accounting for approximately 2% of the total number of foot fractures. Most calcaneus fractures are closed injuries, meaning the skin is intact. When the skin around the calcaneus fracture is broken, this may represent an open fracture, also called a compound fracture. An open fracture of the calcaneus is an emergency that requires urgent surgery.
ABOUT THE HEEL BONE
The bones of the feet are commonly divided into three parts:
- The hindfoot
- The midfoot
- The forefoot
Seven bones — called tarsals — make up the hindfoot and midfoot. The calcaneus is the largest of the tarsal bones in the foot. The calcaneus is often compared to a hardboiled egg because it has a thin, hard shell on the outside and softer, spongy bone on the inside. When the outer shell is broken, the bone tends to collapse and become fragmented. The calcaneus lies at the back of the foot (hindfoot) below the three bones that make up the ankle joint. These three bones are the:
- Tibia (shinbone)
- Fibula (smaller bone in the lower leg)
- Talus (small foot bone that works as a hinge between the tibia and the fibula)
Together, the calcaneus and the talus form the subtalar joint. The subtalar joint allows side-to-side movement of the hindfoot and is especially important for balance on uneven surfaces.
WHAT IS A CALCANEUS FRACTURE?
Fractures of the calcaneus may or may not involve the subtalar and surrounding joints. Fractures involving the joints (intra-articular fractures) are the most severe calcaneus fractures and include damage to the cartilage (the connective tissue between two bones). If the fracture does involve the joints, there is the potential for long-term consequences, such as arthritis and chronic pain. Fractures that do not involve the joint (extra-articular fractures) include:
- Those caused by trauma, such as avulsion fractures (in which a piece of the bone is pulled off of the calcaneus by the Achilles tendon or a ligament) or crush injuries resulting in multiple fracture fragments
- Stress fractures caused by overuse or mild injury
CAUSES
Males ages 30 to 50 fracture their calcaneal most often of any age group or sex. Calcaneus fractures are commonly suffered by roofers and climbers after a fall, although automobile accidents can also cause such fractures to the heel bone. One’s more likely to get a calcaneus stress fracture if they participate in activities or sports that involve repetitive movement, including:
- Basketball
- Dancing
- Long-distance running
- Soccer
- Track and field sports
Other factors that increase the risk of calcaneus fractures include:
- Having an eating disorder
- Using tobacco or overusing alcohol
- Working a job that involves heavy physical labor
SYMPTOMS
The most common symptom of a calcaneus stress fracture is intense heel pain. One may also have trouble putting weight on the heel. The pain may:
- Affect only one spot of the heel
- Increase when trying to stretch the foot
- Worsen the longer standing
Other symptoms include a heel that is:
- Bruised.
- Flushed or red
- Swollen
- Tender or warm to the touch
NON-SURGICAL TREATMENT
Most people heal from a calcaneus fracture with non-invasive treatment such as RICE-rest, ice, compression, and elevation. Rest (staying off the injured foot) is needed to allow the fracture to heal. Ice reduces swelling and pain (apply a bag of ice covered with a thin towel to the affected area). Compression (wrapping the foot in an elastic bandage or wearing a compression stocking). Elevation (keeping the foot even with or slightly above the heart level) also reduces swelling. Sometimes the foot is placed in a cast or cast boot to keep the fractured bone from moving. Crutches may be needed to avoid weight-bearing. If needed, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or other pain medication may be recommended.
WHEN IS SURGERY INDICATED?
While most calcaneus fractures can heal without surgery, sometimes they do not heal, or they might heal in a position that causes chronic pain or trouble with walking or wearing shoes. Some calcaneus fractures can be treated by manipulating the foot while a patient is under anesthesia but not involving surgery. This procedure is called closed reduction. If such a procedure does not treat the fracture or the fracture is more extensive, then surgery may be required, called an open reduction. Surgery may be recommended immediately after a fracture or a few weeks later to allow the inflammation to decrease. In severe cases, further surgery may be required to fuse the subtalar joint. The goal of calcaneus fracture surgery is to restore the shape of the heel bone as close to normal as possible. Restoration of normal alignment and contour is considered the best way to restore function and minimize pain.
GETTING THE RIGHT DIAGNOSIS. GETTING THE RIGHT DOCTOR.
The foot and ankle surgeons at Advanced Orthopedic in Denver, Parker, and Aurora, Colorado, are leading experts in foot and ankle care who treat all conditions from the simple to the complex, including calcaneus fractures. After a detailed examination, your surgeon may order tests, including X-rays, CT scans, or MRIs, to provide enhanced images of your feet to help them determine the extent of the injury. Having the most experienced surgeon is key because of all the long-term complications that can arise from getting an inaccurate diagnosis. At Advanced Orthopedic, you can feel sure that you are getting the best treatment for your specific injury, the kind of care that will get you back on your feet and back to life. Schedule an appointment today with one of our foot and ankle experts.